Symmetry (physics)
In physics, symmetry includes all features of a physical system that exhibit the property of symmetry—that is, under certain transformations, aspects of these systems are "unchanged", according to a particular observation. A symmetry of a physical system is a physical or mathematical feature of the system (observed or intrinsic) that is "preserved" under some change.
A family of particular transformations may be continuous (such as rotation of a circle) or discrete (e.g., reflection of a bilaterally symmetric figure, or rotation of a regular polygon). Continuous and discrete transformations give rise to corresponding types of symmetries. Continuous symmetries can be described by Lie groups while discrete symmetries are described by finite groups (see Symmetry group). Symmetries are frequently amenable to mathematical formulation such as group representations and can be exploited to simplify many problems.
An important example of such symmetry is the invariance of the form of physical laws under arbitrary differentiable coordinate transformations.
Contents |
Symmetry as invariance
Invariance is specified mathematically by transformations that leave some quantity unchanged. This idea can apply to basic real-world observations. For example, temperature may be constant throughout a room. Since the temperature is independent of position within the room, the temperature is invariant under a shift in the measurer's position.
Similarly, a uniform sphere rotated about its center will appear exactly as it did before the rotation. The sphere is said to exhibit spherical symmetry. A rotation about any axis of the sphere will preserve how the sphere "looks".
Invariance in force
The above ideas lead to the useful idea of invariance when discussing observed physical symmetry; this can be applied to symmetries in forces as well.
For example, an electric field due to a wire is said to exhibit cylindrical symmetry, because the electric field strength at a given distance r from the electrically charged wire of infinite length will have the same magnitude at each point on the surface of a cylinder (whose axis is the wire) with radius r. Rotating the wire about its own axis does not change its position or charge density, hence it will preserve the field. The field strength at a rotated position is the same. Suppose some configuration of charges (may be non-stationary) produce an electric field in some direction, then rotating the configuration of the charges (without disturbing the internal dynamics that produces the particular field) will lead to a net rotation of the direction of the electric field.These two properties are interconnected through the more general property that rotating any system of charges causes a corresponding rotation of the electric field.
In Newton's theory of mechanics, given two bodies, each with mass m, starting from rest at the origin and moving along the x-axis in opposite directions, one with speed v1 and the other with speed v2 the total kinetic energy of the system (as calculated from an observer at the origin) is 1⁄2m(v12 + v22) and remains the same if the velocities are interchanged. The total kinetic energy is preserved under a reflection in the y-axis.
The last example above illustrates another way of expressing symmetries, namely through the equations that describe some aspect of the physical system. The above example shows that the total kinetic energy will be the same if v1 and v2 are interchanged.
Local and global symmetries
Symmetries may be broadly classified as global or local. A global symmetry is one that holds at all points of spacetime, whereas a local symmetry is one that has a different symmetry transformation at different points of spacetime; specifically a local symmetry transformation is parameterised by the spacetime co-ordinates. Local symmetries play an important role in physics as they form the basis for gauge theories.
Continuous symmetries
The two examples of rotational symmetry described above - spherical and cylindrical - are each instances of continuous symmetry. These are characterised by invariance following a continuous change in the geometry of the system. For example, the wire may be rotated through any angle about its axis and the field strength will be the same on a given cylinder. Mathematically, continuous symmetries are described by continuous or smooth functions. An important subclass of continuous symmetries in physics are spacetime symmetries.
Spacetime symmetries
Continuous spacetime symmetries are symmetries involving transformations of space and time. These may be further classified as spatial symmetries, involving only the spatial geometry associated with a physical system; temporal symmetries, involving only changes in time; or spatio-temporal symmetries, involving changes in both space and time.
- Time translation: A physical system may have the same features over a certain interval of time
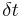 ; this is expressed mathematically as invariance under the transformation
; this is expressed mathematically as invariance under the transformation 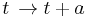 for any real numbers t and a in the interval. For example, in classical mechanics, a particle solely acted upon by gravity will have gravitational potential energy
for any real numbers t and a in the interval. For example, in classical mechanics, a particle solely acted upon by gravity will have gravitational potential energy 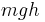 when suspended from a height
when suspended from a height 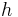 above the Earth's surface. Assuming no change in the height of the particle, this will be the total gravitational potential energy of the particle at all times. In other words, by considering the state of the particle at some time (in seconds)
above the Earth's surface. Assuming no change in the height of the particle, this will be the total gravitational potential energy of the particle at all times. In other words, by considering the state of the particle at some time (in seconds) 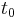 and also at
and also at 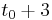 , say, the particle's total gravitational potential energy will be preserved.
, say, the particle's total gravitational potential energy will be preserved.
- Spatial translation: These spatial symmetries are represented by transformations of the form
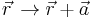 and describe those situations where a property of the system does not change with a continuous change in location. For example, the temperature in a room may be independent of where the thermometer is located in the room.
and describe those situations where a property of the system does not change with a continuous change in location. For example, the temperature in a room may be independent of where the thermometer is located in the room.
- Spatial rotation: These spatial symmetries are classified as proper rotations and improper rotations. The former are just the 'ordinary' rotations; mathematically, they are represented by square matrices with unit determinant. The latter are represented by square matrices with determinant −1 and consist of a proper rotation combined with a spatial reflection (inversion). For example, a sphere has proper rotational symmetry. Other types of spatial rotations are described in the article Rotation symmetry.
- Poincaré transformations: These are spatio-temporal symmetries which preserve distances in Minkowski spacetime, i.e. they are isometries of Minkowski space. They are studied primarily in special relativity. Those isometries that leave the origin fixed are called Lorentz transformations and give rise to the symmetry known as Lorentz covariance.
- Projective symmetries: These are spatio-temporal symmetries which preserve the geodesic structure of spacetime. They may be defined on any smooth manifold, but find many applications in the study of exact solutions in general relativity.
- Inversion transformations: These are spatio-temporal symmetries which generalise Poincaré transformations to include other conformal one-to-one transformations on the space-time coordinates. Lengths are not invariant under inversion transformations but there is a cross-ratio on four points that is invariant.
Mathematically, spacetime symmetries are usually described by smooth vector fields on a smooth manifold. The underlying local diffeomorphisms associated with the vector fields correspond more directly to the physical symmetries, but the vector fields themselves are more often used when classifying the symmetries of the physical system.
Some of the most important vector fields are Killing vector fields which are those spacetime symmetries that preserve the underlying metric structure of a manifold. In rough terms, Killing vector fields preserve the distance between any two points of the manifold and often go by the name of isometries. The article Isometries in physics discusses these symmetries in more detail.
Discrete symmetries
A discrete symmetry is a symmetry that describes non-continuous changes in a system. For example, a square possesses discrete rotational symmetry, as only rotations by multiples of right angles will preserve the square's original appearance. Discrete symmetries sometimes involve some type of 'swapping', these swaps usually being called reflections or interchanges.
- Time reversal: Many laws of physics describe real phenomena when the direction of time is reversed. Mathematically, this is represented by the transformation,
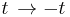 . For example, Newton's second law of motion still holds if, in the equation
. For example, Newton's second law of motion still holds if, in the equation 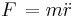 ,
, 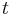 is replaced by
is replaced by 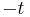 . This may be illustrated by describing the motion of a particle thrown up vertically (neglecting air resistance). For such a particle, position is symmetric with respect to the instant that the object is at its maximum height. Velocity at reversed time is reversed.
. This may be illustrated by describing the motion of a particle thrown up vertically (neglecting air resistance). For such a particle, position is symmetric with respect to the instant that the object is at its maximum height. Velocity at reversed time is reversed.
- Spatial inversion: These are represented by transformations of the form
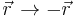 and indicate an invariance property of a system when the coordinates are 'inverted'.
and indicate an invariance property of a system when the coordinates are 'inverted'.
- Glide reflection: These are represented by a composition of a translation and a reflection. These symmetries occur in some crystals and in some planar symmetries, known as wallpaper symmetries.
C, P, and T symmetries
The Standard model of particle physics has three related natural near-symmetries. These state that the actual universe about us is indistinguishable from one where:
- Every particle is replaced with its antiparticle. This is C-symmetry (charge symmetry);
- Everything appears as if reflected in a mirror. This is P-symmetry (parity symmetry);
- The direction of time is reversed. This is T-symmetry (time symmetry).
T-symmetry is counterintuitive (surely the future and the past are not symmetrical) but explained by the fact that the Standard model describes local properties, not global ones like entropy. To properly reverse the direction of time, one would have to put the big bang and the resulting low-entropy state in the "future." Since we perceive the "past" ("future") as having lower (higher) entropy than the present (see perception of time), the inhabitants of this hypothetical time-reversed universe would perceive the future in the same way as we perceive the past.
These symmetries are near-symmetries because each is broken in the present-day universe. However, the Standard Model predicts that the combination of the three (that is, the simultaneous application of all three transformations) must be a symmetry, called CPT symmetry. CP violation, the violation of the combination of C- and P-symmetry, is necessary for the presence of significant amounts of baryonic matter in the universe and thus is a prerequisite for the existence of life. CP violation is a fruitful area of current research in particle physics.
Supersymmetry
A type of symmetry known as supersymmetry has been used to try to make theoretical advances in the standard model. Supersymmetry is based on the idea that there is another physical symmetry beyond those already developed in the standard model, specifically a symmetry between bosons and fermions. Supersymmetry asserts that each type of boson has, as a supersymmetric partner, a fermion, called a superpartner, and vice versa. Supersymmetry has not yet been experimentally verified: no known particle has the correct properties to be a superpartner of any other known particle. If superpartners exist they must have masses greater than current particle accelerators can generate.
Mathematics of physical symmetry
The transformations describing physical symmetries typically form a mathematical group. Group theory is an important area of mathematics for physicists.
Continuous symmetries are specified mathematically by continuous groups (called Lie groups). Many physical symmetries are isometries and are specified by symmetry groups. Sometimes this term is used for more general types of symmetries. The set of all proper rotations (about any angle) through any axis of a sphere form a Lie group called the special orthogonal group 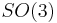 . (The 3 refers to the three-dimensional space of an ordinary sphere.) Thus, the symmetry group of the sphere with proper rotations is
. (The 3 refers to the three-dimensional space of an ordinary sphere.) Thus, the symmetry group of the sphere with proper rotations is 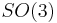 . Any rotation preserves distances on the surface of the ball. The set of all Lorentz transformations form a group called the Lorentz group (this may be generalised to the Poincaré group).
. Any rotation preserves distances on the surface of the ball. The set of all Lorentz transformations form a group called the Lorentz group (this may be generalised to the Poincaré group).
Discrete symmetries are described by discrete groups. For example, the symmetries of an equilateral triangle are described by the symmetric group 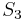 .
.
An important type of physical theory based on local symmetries is called a gauge theory and the symmetries natural to such a theory are called gauge symmetries. Gauge symmetries in the Standard model, used to describe three of the fundamental interactions, are based on the SU(3) × SU(2) × U(1) group. (Roughly speaking, the symmetries of the SU(3) group describe the strong force, the SU(2) group describes the weak interaction and the U(1) group describes the electromagnetic force.)
Also, the reduction by symmetry of the energy functional under the action by a group and spontaneous symmetry breaking of transformations of symmetric groups appear to elucidate topics in particle physics (for example, the unification of electromagnetism and the weak force in physical cosmology).
Conservation laws and symmetry
The symmetry properties of a physical system are intimately related to the conservation laws characterizing that system. Noether's theorem gives a precise description of this relation. The theorem states that each continuous symmetry of a physical system implies that some physical property of that system is conserved. Conversely, each conserved quantity has a corresponding symmetry. For example, the isometry of space gives rise to conservation of (linear) momentum, and isometry of time gives rise to conservation of energy.
The following table summarizes some fundamental symmetries and the associated conserved quantity.
| Class | Invariance | Conserved quantity |
| Proper orthochronous Lorentz symmetry |
translation in time (homogeneity) |
energy |
| translation in space (homogeneity) |
linear momentum | |
| rotation in space (isotropy) |
angular momentum | |
| Discrete symmetry | P, coordinate inversion | spatial parity |
| C, charge conjugation | charge parity | |
| T, time reversal | time parity | |
| CPT | product of parities | |
| Internal symmetry (independent of spacetime coordinates) |
U(1) gauge transformation | electric charge |
| U(1) gauge transformation | lepton generation number | |
| U(1) gauge transformation | hypercharge | |
| U(1)Y gauge transformation | weak hypercharge | |
| U(2) [U(1) × SU(2)] | electroweak force | |
| SU(2) gauge transformation | isospin | |
| SU(2)L gauge transformation | weak isospin | |
| P × SU(2) | G-parity | |
| SU(3) "winding number" | baryon number | |
| SU(3) gauge transformation | quark color | |
| SU(3) (approximate) | quark flavor | |
| S(U(2) × U(3)) [ U(1) × SU(2) × SU(3)] |
Standard Model |
See also
- Conservation law
- Conserved current
- Coordinate-free
- Covariance and contravariance
- Diffeomorphism
- Fictitious force
- Galilean invariance
- Gauge theory
- General covariance
- Harmonic coordinate condition
- Inertial frame of reference
- Lie group
- List of mathematical topics in relativity
- Lorentz covariance
- Noether's theorem
- Poincaré group
- Special relativity
- Spontaneous symmetry breaking
- Standard model
- Standard model (mathematical formulation)
- Symmetry breaking
- Wheeler–Feynman Time-Symmetric Theory
References
General readers
- Leon Lederman and Christopher T. Hill (2005) Symmetry and the Beautiful Universe. Amherst NY: Prometheus Books.
- Schumm, Bruce (2004) Deep Down Things. Johns Hopkins Univ. Press.
- Victor J. Stenger (2000) Timeless Reality: Symmetry, Simplicity, and Multiple Universes. Buffalo NY: Prometheus Books. Chpt. 12 is a gentle introduction to symmetry, invariance, and conservation laws.
- Anthony Zee (2007) Fearful Symmetry: The search for beauty in modern physics, 2nd ed. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-00946-9. 1986 1st ed. published by Macmillan.
Technical
- Brading, K., and Castellani, E., eds. (2003) Symmetries in Physics: Philosophical Reflections. Cambridge Univ. Press.
- -------- (2007) "Symmetries and Invariances in Classical Physics" in Butterfield, J., and John Earman, eds., Philosophy of Physic Part B. North Holland: 1331-68.
- Debs, T. and Redhead, M. (2007) Objectivity, Invariance, and Convention: Symmetry in Physical Science. Harvard Univ. Press.
- John Earman (2002) "Laws, Symmetry, and Symmetry Breaking: Invariance, Conservations Principles, and Objectivity." Address to the 2002 meeting of the Philosophy of Science Association.
- Mainzer, K. (1996) Symmetries of nature. Berlin: De Gruyter.
- Thompson, William J. (1994) Angular Momentum: An Illustrated Guide to Rotational Symmetries for Physical Systems. Wiley. ISBN 0-471-55264.
- Bas Van Fraassen (1989) Laws and symmetry. Oxford Univ. Press.
- Eugene Wigner (1967) Symmetries and Reflections. Indiana Univ. Press.
External links
- Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy: "Symmetry" -- by K. Brading and E. Castellani.
- Pedagogic Aids to Quantum Field Theory Click on link to Chapter 6: Symmetry, Invariance, and Conservation for a simplified, step-by-step introduction to symmetry in physics.